With AI, we’re moving toward what you might call an ‘instantaneous healthcare system.’ No more long and frustrating waits for appointments or insurance claims. AI is automating everything from analyzing medical images and FDA approvals to managing referrals. It’s not just paperwork – AI is driving groundbreaking discoveries in novel treatments and offering personalized care via remote gadgets, even helping those in the front of the house.
AI is transforming healthcare by predicting risks, improving patient care, and streamlining various processes. It prevents hospital-acquired conditions, optimizes clinical pathways, and collaborates with humans in healthcare settings.
Additionally, AI assists with medication dispensing and enhances health monitoring. The technology is also simplifying claims processing clinical documentation and efficiently managing medical records and revenue cycles.
Today, in the healthcare industry, AI is helping healthcare practitioners optimize workflows and reduce costs in four major ways:
In 1950, the amount of medical information available to clinicians doubled every 50 years. In 2021, it was doubling every 60 days. Clinicians and physicians struggle to keep up with this exponential growth in medical knowledge.
On the other hand, the biggest challenge to treating a patient is handling a large amount of data, usually generated by various sources, such as EHRs, medical devices, lab tests, imaging, and patients’ previous sessions and appointments.
AI tools create specialized search solutions for quick access to patient data from various sources, including EHRs, medical devices, and lab tests, encompassing text structured and unstructured information.
These AI-driven search engines, powered by NLP and Computer Vision, retrieve patient records and research articles and offer personalized treatment suggestions, facilitating ongoing patient medical history summaries.
Here are two examples:
Google AI Health – Google Health provides AI-powered tools to aid healthcare professionals in their research, securely supporting doctors, nurses, and more.
IBM’s Watson – IBM’s Watson platform empowers healthcare organizations to process extensive patient data, exceeding human capabilities. It comprehensively analyzes global medical data, from publications to symptoms and treatment effectiveness studies.
“I believe AI has the potential to transform people’s health on a planetary scale. If developed boldly and responsibly, AI will be a powerful force for health equity, improving outcomes for everyone, everywhere.“
Dr. Karen DeSalvo, Google’s Chief Health Officer
NLP is a subset of AI that deals with computer-human language interaction. It can extract information from unstructured medical data, as mentioned above. This information is then organized and presented in a format clinicians can easily understand and utilize.
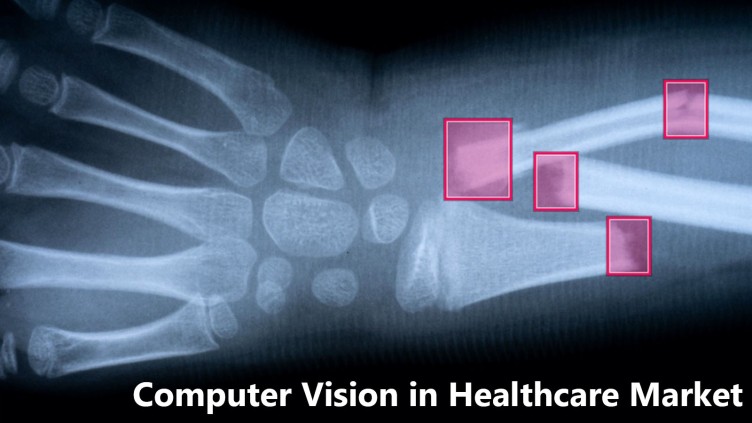
Computer Vision, another branch of AI, focuses on computers’ ability to understand and interpret images and videos. In healthcare, it’s used to analyze medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, identifying diseases and anomalies.
The science and engineering of creating intelligent computers from algorithms or a set of rules to replicate human cognitive processes like learning and problem-solving are now powered by AI. Similarly, clinical decision support (CDS) uses data and algorithms to generate insights, recommendations, or alerts to improve the quality and safety of care.
Sounds great, but the glitch starts from the time when providers need to go through every piece of data. Providers must ensure they don’t miss a single piece of information, which is, TBH, humanly impossible when a single patient generates close to 80 megabytes each year. Not to mention the amount of legacy EHR data. Rendering a conclusion is extremely hard without summarising these mountains of data.
AI automates data parsing and analysis, extracting critical insights and creating concise patient medical history summaries, identifying trends, anomalies, and potential risks. It can suggest tests, interventions, and action items, streamlining patient care coordination.
AI-enabled solutions, like advanced medical imaging, enhance diagnostics and interventions by performing repetitive tasks with high accuracy, aiding in early issue identification. Machine learning and predictive analytics enable risk assessment, condition diagnosis, and treatment suggestions, improving clinical judgments.
For example, an Israeli startup developed AI capable of detecting bone issues, brain bleeds, and cancer in X-rays and scans, matching or exceeding human performance. AI also supports early disease identification, as demonstrated by Sepsis Watch in Duke University Health System’s ER, helping professionals identify sepsis early, a major cause of hospital fatalities.
Healthcare admin tasks can be a hassle. They involve scheduling, billing, coding, claims processing, and ensuring everything is compliant. It’s not only dull but also prone to human errors. AI can automate them using Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to understand and execute instructions, queries, or rules.
Machine Learning is good at spotting patterns in massive amounts of data and keeps improving as it learns more. It can double-check insurance eligibility, create invoices, code medical procedures, or catch any mistakes – which means we can be way more efficient and accurate. This leaves more time to focus on more critical tasks.
Healthcare leaders are prioritizing automating business processes, including RCM, for cost reduction. For instance, automating eligibility and benefits verification, the initial administrative step in patient encounters, can save $6.52 per transaction, totaling $4 billion annually. Machine learning tools prioritize work and minimize errors based on payment likelihood or account age.
AI-driven revenue cycle management streamlines healthcare operations in several key ways:
Nobody likes paperwork. Step up, ChatGPT. In March 2023, Nuance and Microsoft introduced DAX Express, a clinical documentation app integrating advanced AI, including OpenAI’s GPT-4 model. DAX Express streamlines administrative tasks, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care. This innovation is available to over 550,000 Dragon Medical users, leveraging Microsoft Azure capabilities.
With healthcare spanning a lifetime, care navigation acts as a GPS, guiding patients to the right providers, optimizing care, and reducing costs. AI enhances this by providing 24/7 remote accessibility via mobile apps, excelling in conversational chat and natural language processing for streamlined patient interactions and assessments.
When integrated with search and summarization, AI accelerates communication with healthcare providers. It offers real-time, research-backed care navigation, plays a vital role in telemedicine, supports remote patient monitoring mental health services, and identifies situations needing human intervention. Let’s delve into the three key steps in care navigation.
The first step is understanding the patient’s needs. This involves looking at their medical history, current health status, and social factors affecting their health.
With proper care navigation, patient experiences better outcomes. Better outcomes also translate to fewer hospital readmissions, saving money for both patients and providers. A win-win for all involved.
‘AI stands as one of the most revolutionary technologies in our era, and its most urgent domain of application is undeniably within the realm of healthcare.’
Satya Nadella, Chief Executive Officer of Microsoft
There are plenty of other barriers in healthcare that AI is helping to cure, ranging from communication, bias, responsibility, staffing, and misinformation. Let’s look at these examples.
According to findings, 55% of patients will likely switch providers if their communication preferences are not met. Patients want face-to-face interaction with providers as they don’t want to miss a single piece of info about themself and their health (But within the comfort of their living room).
How AI Chatbots Help:
There is a particular bias and stigma that can have detrimental effects on a patient’s access to care. It often deters individuals from seeking specialized support, like mental healthcare services or hormone replacement therapy, due to the fear of being judged or not treated well. Fortunately, healthcare leaders are taking steps to combat this issue.
For example, Myongji Hospital in South Korea collaborates with robot maker Whydots to create an AI-driven care robot, “PIO,” to assist dementia patients. This parrot-like robot recognizes patients’ faces and expressions, uses LED eyes and body movements to convey emotions, and provides emotional support for early dementia patients, showcasing how technology can enhance healthcare and patient well-being.
Despite over a decade of focus, AI adoption in healthcare still needs to be improved. Too frequently, attempts are made to fit square pegs into round holes. Those AI solutions ignored the local context, such as clinical workflows, user needs, trust, safety, and ethical implications.
Recognizing the prevalent issue of interpretability in neural networks, efforts are directed toward enhancing trustworthiness in AI. This includes the development of interpretable AI to clarify the rationale behind AI recommendations for healthcare professionals. Acknowledging the significance of data authenticity is crucial in this context, as emphasized by the founder of an algorithmic risk management consulting firm.
“You wouldn’t let your company design a car and send it out without knowing whether it’s safe. You have to design it with safety standards in mind,” she says. “By the same token, algorithms have to be designed with fairness and legality in mind, with standards that are understandable to everyone, from the business leader to the people being scored.”
Cathy O’Neil, Mathematician, Data Scientist & Author
Healthcare institutions across the country are facing severe staffing shortages. 2034, there is potential for a crisis, with an expected shortage of 124,000 physicians and over 600,000 nurses projected to leave the field by 2027.
Mudit Garg, CEO of Qventus, said, “Hospitals have closed or stopped providing essential services, including maternity care and emergency rooms. Healthcare systems can boost surgical revenue by maximizing the use of operating rooms through better scheduling thanks to AI-powered care automation.
Hospitals can reduce the typical patient stay by automating some aspects of the discharge process. Hospitals are dealing with a personnel shortage worsened by the Covid-19 pandemic.
They need to free up their providers to focus on the most crucial duties because they no longer have the bodies to sling at routine tasks. AI and automation are bridging these workforce gaps and streamlining administrative tasks within the healthcare industry.
“Access to information equals freedom of choice,” said Silvia Taylor, Executive VP, chief corporate affairs and advocacy officer at Novavax, in her podcast – ‘Access to Information Equals Freedom of Choice’.
There is an endless amount of health content to consume online. Patients are flooded with ads stemming from influencers and brands, but unfortunately, much of this information is inaccurate. Ensuring patients have access to accurate and reliable health information is crucial in an age of information overload.
This problem becomes even more pronounced when well-intentioned misinformation spreads through various online platforms. Health providers must play a key role in guiding patients toward trustworthy sources, educating them on how to evaluate online content critically, and making sure they can make informed decisions about their wellness.
This patient empowerment can lead to better health outcomes and increased confidence in navigating the vast sea of online health information.